主流编译器下查看内存布局
gcc 编译器:
1
2
3
4
5
| # 低版本
gcc++ -fdump-class-hierarchy xxx.cpp
# 高版本
gcc++ -fdump-lang-class xxx.cpp
|
clang 编译器:
1
2
3
4
5
| # 查看对象布局
clang -Xclang -fdump-record-layouts -stdlib=libc++ xxx.cpp
# 查看虚函数表布局
clang -Xclang -fdump-vtable-layouts -stdlib=libc++ xxx.cpp
|
msvc 编译器:
1
2
3
4
5
| # 输出单个类相关布局(VS项目属性 -> C/C++ -> 命令行 -> 其他选项)
/d1 reportSingleClassLayout<类名>
# 输出所有类相关布局(VS项目属性 -> C/C++ -> 命令行 -> 其他选项)
/d1 reportAllClassLayout
|
常见内存布局(Clang, 64位)
测试代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| class Base1
{
public:
Base1():B1(0) {};
virtual ~Base1() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB1() {};
public:
int B1;
};
class Base2
{
public:
Base2() :B2(0) {};
virtual ~Base2() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB2() {};
public:
int B2;
};
class Derive1 : public Base1
{
public:
Derive1():D1(0) {};
virtual ~Derive1() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB1() {};
virtual void FuncD1() {};
public:
int D1;
};
class Derive2 : public Base1, public Base2
{
public:
Derive2() :D2(0) {};
virtual ~Derive2() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB1() {};
virtual void FuncB2() {};
virtual void FuncD2() {};
public:
int D2;
};
class VDerive1 : virtual public Base1
{
public:
VDerive1() :VD1(0) {};
virtual ~VDerive1() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB1() {};
virtual void FuncVD1() {};
public:
int VD1;
};
class VDerive2 : virtual public Base1
{
public:
VDerive2() :VD2(0) {};
virtual ~VDerive2() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB1() {};
virtual void FuncVD2() {};
public:
int VD2;
};
class DiamondSon: public VDerive1, public VDerive2
{
public:
DiamondSon():Diamond(0) {};
virtual ~DiamondSon() {};
public:
virtual void FuncB1() {};
virtual void FuncDiamond() {};
public:
int Diamond;
};
|
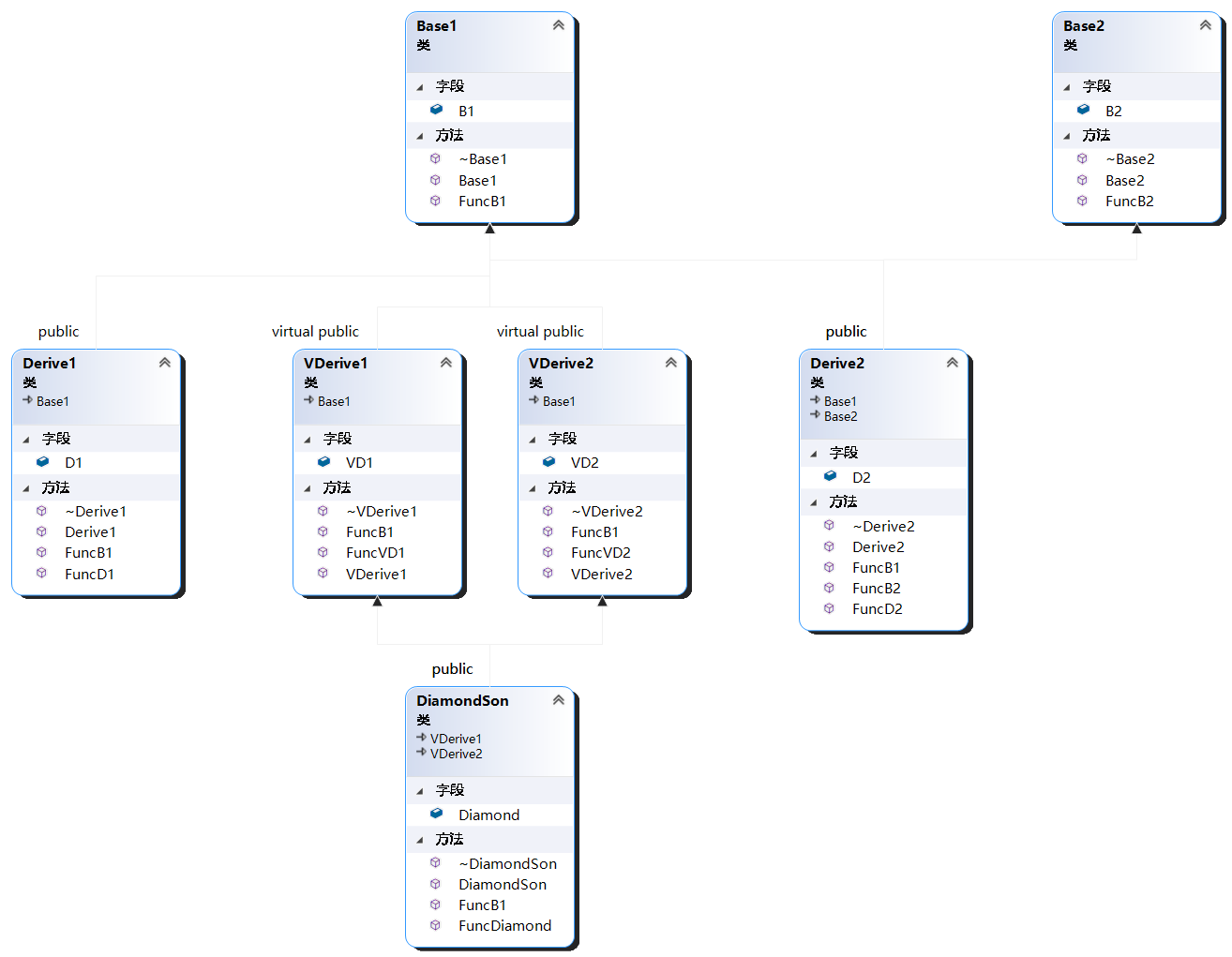
- 虚基类:Base1 和 Base2
- 普通继承: Derive1 -> Base1
- 多继承: Derive2 -> Base1, Base2
- 虚继承: VDerive1 –> Base1 和 VDerive2 –> Base1
- 菱形继承: DiamondSon -> VDerive1, VDerive2 –> Base1
虚基类内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
| *** Dumping AST Record Layout
0 | class Base1
0 | (Base1 vtable pointer)
8 | int B1
| [sizeof=16, dsize=12, align=8,
| nvsize=12, nvalign=8]
|
由虚基类(Base1 或 Base2)的内存布局可以看出,其对象大小为 16,在对象的头部,前8个字节是虚函数表的指针(64位),指向虚函数的相应函数指针地址,成员变量 B1 占 4 个字节,按照 8 字节对齐,总大小为 16。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Vtable for 'Base1' (5 entries).
0 | offset_to_top (0)
1 | Base1 RTTI
-- (Base1, 0) vtable address --
2 | Base1::~Base1() [complete]
3 | Base1::~Base1() [deleting]
4 | void Base1::FuncB1()
VTable indices for 'Base1' (3 entries).
0 | Base1::~Base1() [complete]
1 | Base1::~Base1() [deleting]
2 | void Base1::FuncB1()
|
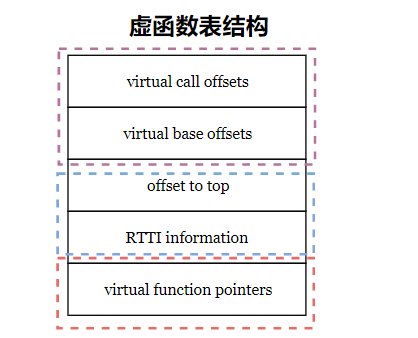
由虚函数表布局可以看出,虚函数表包括三部分:offset_to_top、RTTI、虚函数地址/指针。(虚函数表指针 vfptr 直接指向虚函数地址,不包含前面的部分)
- offset_to_top(0):表示实际类型起始地址到当前这个形式类型起始地址的偏移量。由于当前类型不存在继承关系,所以偏移量为 0。
- RTTI指针:指向存储运行时类型信息(type_info)的地址,用于运行时类型识别,用于 typeid 和dynamic_cast。
为什么有两个析构函数:一个标志为deleting,一个标志为complete,因为对象有两种构造方式,栈构造和堆构造,所以对应的实现上,对象也有两种析构方式,其中堆上对象的析构和栈上对象的析构不同之处在于,栈内存的析构不需要执行 delete 函数,会自动被回收。
为什么基类析构函数要是虚函数:一般基类的析构函数都要设置成虚函数,因为如果不设置成虚函数,在析构的过程中只会调用到基类的析构函数而不会调用到子类的析构函数,可能会产生内存泄漏。
单链继承内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| *** Dumping AST Record Layout
0 | class Derive1
0 | class Base1 (primary base)
0 | (Base1 vtable pointer)
8 | int B1
12 | int D1
| [sizeof=16, dsize=16, align=8,
| nvsize=16, nvalign=8]
|
由 Derive1 的内存布局可以看出,其对象大小为 16,在对象的头部,前8个字节是虚函数表的指针(64位),然后依次是基类和自身成员变量 B1、D1 各占 4 个字节,总大小为 16。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| Vtable for 'Derive1' (6 entries).
0 | offset_to_top (0)
1 | Derive1 RTTI
-- (Base1, 0) vtable address --
-- (Derive1, 0) vtable address --
2 | Derive1::~Derive1() [complete]
3 | Derive1::~Derive1() [deleting]
4 | void Derive1::FuncB1()
5 | void Derive1::FuncD1()
VTable indices for 'Derive1' (4 entries).
0 | Derive1::~Derive1() [complete]
1 | Derive1::~Derive1() [deleting]
2 | void Derive1::FuncB1()
3 | void Derive1::FuncD1()
|
- offset_to_top(0):单链继承的情况下,动态向下转换和向上转换时,不需要对this指针的地址做出任何修改,只需要对其重新“解释”,所以 offsets_to_top 为 0。
- RTTI 中有了两项,表明此时子类中 Base1、Derive1 虚函数表位置是相同的。当基类的引用/指针指向子类对象时,会通过虚函数表调用子类的虚函数。
- 由于子类重写了基类的函数(FuncB1),基类对应位置的虚函数指针(Base1::FuncB1)会被替换成子类的虚函数指针(Derive1::FuncB1)。
多继承内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| *** Dumping AST Record Layout
0 | class Derive2
0 | class Base1 (primary base)
0 | (Base1 vtable pointer)
8 | int B1
16 | class Base2 (base)
16 | (Base2 vtable pointer)
24 | int B2
28 | int D2
| [sizeof=32, dsize=32, align=8,
| nvsize=32, nvalign=8]
|
由 Derive2 的内存布局可以看出,多继承的情况下,内存布局中会存在多个虚函数表指针。内存中虚函数表和成员的顺序按照声明的继承顺序排列。继承的第一个类,被标记为 primary base。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| Vtable for 'Derive2' (12 entries).
0 | offset_to_top (0)
1 | Derive2 RTTI
-- (Base1, 0) vtable address --
-- (Derive2, 0) vtable address --
2 | Derive2::~Derive2() [complete]
3 | Derive2::~Derive2() [deleting]
4 | void Derive2::FuncB1()
5 | void Derive2::FuncB2()
6 | void Derive2::FuncD2()
7 | offset_to_top (-16)
8 | Derive2 RTTI
-- (Base2, 16) vtable address --
9 | Derive2::~Derive2() [complete]
[this adjustment: -16 non-virtual]
10 | Derive2::~Derive2() [deleting]
[this adjustment: -16 non-virtual]
11 | void Derive2::FuncB2()
[this adjustment: -16 non-virtual]
Thunks for 'Derive2::~Derive2()' (1 entry).
0 | this adjustment: -16 non-virtual
Thunks for 'void Derive2::FuncB2()' (1 entry).
0 | this adjustment: -16 non-virtual
VTable indices for 'Derive2' (5 entries).
0 | Derive2::~Derive2() [complete]
1 | Derive2::~Derive2() [deleting]
2 | void Derive2::FuncB1()
3 | void Derive2::FuncB2()
4 | void Derive2::FuncD2()
|
- offset_to_top(0):表明虚函数表地址距离对象顶部的偏移量,根据下面相邻的 RTTI 可以知道 primary base (Base1)和子类(Derive2)会共用此虚函数表,然后从对象的内存分布可看出,Derive2 和 Base1 在对象头部,所以是 0。
- 第一个RTTI指针:表明下面为 Base1、Derive2 的虚函数表。当 primary base 类型的引用/指针指向子类对象时,会通过此虚函数表调用子类的虚函数。
- 第一个虚函数表:包含 Base1、Derive2 中声明的虚函数的指针,子类已重写的会替换为对应的子类地址。
- offset_to_top(-16):表明虚函数表地址距离对象顶部的偏移量。根据下面相邻的 RTTI 可以知道 base (Base2)会使用此虚函数表,然后从对象的内存布局可知 Base2 的地址偏移是16,当通过指向子类对象的 Base2 指针调用虚函数时,this 指针需要向上调整 -16,转换为真实类型的地址,方能正确调用。
- 第二个RTTI指针:表明下面为 Base2 的虚函数表。
- 第二个虚函数表:包含 Base2 中声明的虚函数的指针,子类已重写的会替换为对应的子类地址。带 adjustment 标记的函数表示调用时需要进行 this 指针调整。
虚继承内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| *** Dumping AST Record Layout
0 | class VDerive1
0 | (VDerive1 vtable pointer)
8 | int VD1
16 | class Base1 (virtual base)
16 | (Base1 vtable pointer)
24 | int B1
| [sizeof=32, dsize=28, align=8,
| nvsize=12, nvalign=8]
|
虚继承下,对象布局和普通单继承有所不同,普通单继承下子类(Derive1)和基类共用一个虚表地址,而在虚继承下,子类(VDerive1)和虚基类分别有一个虚表地址的指针。内存中,虚继承的基类内容放在最后面。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| Vtable for 'VDerive1' (14 entries).
0 | vbase_offset (16)
1 | offset_to_top (0)
2 | VDerive1 RTTI
-- (VDerive1, 0) vtable address --
3 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [complete]
4 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [deleting]
5 | void VDerive1::FuncB1()
6 | void VDerive1::FuncVD1()
7 | vcall_offset (-16)
8 | vcall_offset (-16)
9 | offset_to_top (-16)
10 | VDerive1 RTTI
-- (Base1, 16) vtable address --
11 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [complete]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
12 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [deleting]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
13 | void VDerive1::FuncB1()
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -32 vcall offset offset]
Virtual base offset offsets for 'VDerive1' (1 entry).
Base1 | -24
Thunks for 'VDerive1::~VDerive1()' (1 entry).
0 | this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset
Thunks for 'void VDerive1::FuncB1()' (1 entry).
0 | this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -32 vcall offset offset
VTable indices for 'VDerive1' (4 entries).
0 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [complete]
1 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [deleting]
2 | void VDerive1::FuncB1()
3 | void VDerive1::FuncVD1()
|
- vbase_offset(16):在对象布局中,指向虚基类的虚函数表的指针地址(Base1 vtable pointer)的偏移量,即虚基类相对于当前对象的位置。
- vcall_offset(-16):表示虚基类对象指针修正为实际对象指针,this 要加上的偏移量。vcall_offset 的数量取决于虚基类中虚函数的数量。
菱形继承内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| *** Dumping AST Record Layout
0 | class DiamondSon
0 | class VDerive1 (primary base)
0 | (VDerive1 vtable pointer)
8 | int VD1
16 | class VDerive2 (base)
16 | (VDerive2 vtable pointer)
24 | int VD2
28 | int Diamond
32 | class Base1 (virtual base)
32 | (Base1 vtable pointer)
40 | int B1
| [sizeof=48, dsize=44, align=8,
| nvsize=32, nvalign=8]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
| Vtable for 'DiamondSon' (22 entries).
0 | vbase_offset (32)
1 | offset_to_top (0)
2 | DiamondSon RTTI
-- (DiamondSon, 0) vtable address --
-- (VDerive1, 0) vtable address --
3 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [complete]
4 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [deleting]
5 | void DiamondSon::FuncB1()
6 | void VDerive1::FuncVD1()
7 | void DiamondSon::FuncDiamond()
8 | vbase_offset (16)
9 | offset_to_top (-16)
10 | DiamondSon RTTI
-- (VDerive2, 16) vtable address --
11 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [complete]
[this adjustment: -16 non-virtual]
12 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [deleting]
[this adjustment: -16 non-virtual]
13 | void DiamondSon::FuncB1()
[this adjustment: -16 non-virtual]
14 | void VDerive2::FuncVD2()
15 | vcall_offset (-32)
16 | vcall_offset (-32)
17 | offset_to_top (-32)
18 | DiamondSon RTTI
-- (Base1, 32) vtable address --
19 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [complete]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
20 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [deleting]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
21 | void DiamondSon::FuncB1()
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -32 vcall offset offset]
Virtual base offset offsets for 'DiamondSon' (1 entry).
Base1 | -24
Thunks for 'DiamondSon::~DiamondSon()' (2 entries).
0 | this adjustment: -16 non-virtual
1 | this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset
Thunks for 'void DiamondSon::FuncB1()' (2 entries).
0 | this adjustment: -16 non-virtual
1 | this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -32 vcall offset offset
VTable indices for 'DiamondSon' (4 entries).
0 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [complete]
1 | DiamondSon::~DiamondSon() [deleting]
2 | void DiamondSon::FuncB1()
4 | void DiamondSon::FuncDiamond()
Construction vtable for ('VDerive1', 0) in 'DiamondSon' (14 entries).
0 | vbase_offset (32)
1 | offset_to_top (0)
2 | VDerive1 RTTI
-- (VDerive1, 0) vtable address --
3 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [complete]
4 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [deleting]
5 | void VDerive1::FuncB1()
6 | void VDerive1::FuncVD1()
7 | vcall_offset (-32)
8 | vcall_offset (-32)
9 | offset_to_top (-32)
10 | VDerive1 RTTI
-- (Base1, 32) vtable address --
11 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [complete]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
12 | VDerive1::~VDerive1() [deleting]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
13 | void VDerive1::FuncB1()
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -32 vcall offset offset]
Construction vtable for ('VDerive2', 16) in 'DiamondSon' (14 entries).
0 | vbase_offset (16)
1 | offset_to_top (0)
2 | VDerive2 RTTI
-- (VDerive2, 16) vtable address --
3 | VDerive2::~VDerive2() [complete]
4 | VDerive2::~VDerive2() [deleting]
5 | void VDerive2::FuncB1()
6 | void VDerive2::FuncVD2()
7 | vcall_offset (-16)
8 | vcall_offset (-16)
9 | offset_to_top (-16)
10 | VDerive2 RTTI
-- (Base1, 32) vtable address --
11 | VDerive2::~VDerive2() [complete]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
12 | VDerive2::~VDerive2() [deleting]
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -24 vcall offset offset]
13 | void VDerive2::FuncB1()
[this adjustment: 0 non-virtual, -32 vcall offset offset]
|
虚继承主要解决菱形继承时,产生的空间浪费和二义性。
Linux 对象布局示例
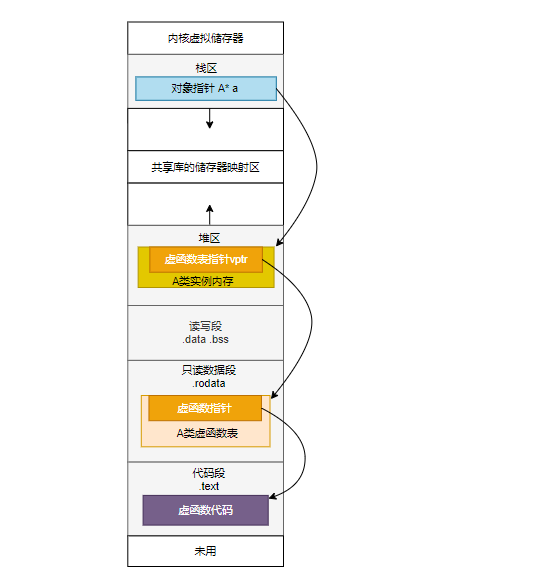
a作为对象指针存储在栈中,指向在堆中的类A的实例内存,其中实例内存布局中有虚函数表指针,指针指向的虚函数表存放在数据段中,虚函数表中的各个函数指针指向的函数在代码段中。
虚函数表结构
参考文档
- https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1755489
- https://juejin.cn/post/6844903666667749389



